Hi there!
Did you know in 2020 guns overtook car crashes to become the leading cause of death for US children and teenagers? While suicides contribute to the toll, the data shows that homicides form the majority of gun-related deaths. With over 390 million guns with American civilians, an average American has more than one gun.
Today’s letter will look into American life expectancy as well as mass shootings, and a lot more. Let's dive in!
Five Stories
'Live free and die?' The sad state of U.S. life expectancy
Selena Simmons-Duffin
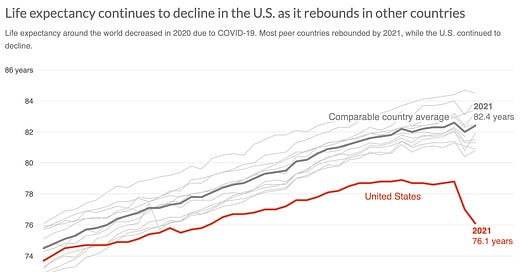
American life expectancy has dropped for two years in a row and is lower than that of many other wealthy countries, according to a landmark study by a panel convened by the National Academy of Sciences and funded by the National Institutes of Health.
The study, called “Shorter Lives, Poorer Health”, found that Americans have more diseases and die younger than their peers because of factors like teen pregnancy, drug overdoses, HIV, fatal car crashes, injuries, and violence. The study also showed that Americans have higher survival after age 75, lower rates of smoking, and higher average household income than other countries, but these achievements are not enough to offset the other problems.
Here’s an interactive visualisation breaking down life expectancy by state (and gender) by CDC.
The terrible numbers that grow with each mass shooting
The Washington Post
Mass shooting statistics in the United States is a web page that shows how often and by whom people are killed in public shootings. It defines a public mass shooting as one in which four or more people were killed, usually by a lone shooter, and excludes shootings tied to robberies or domestic violence.
It uses data from the Gun Violence Archive and starts from Aug. 1, 1966, when a student sniper killed 17 people at the University of Texas. The web page reveals that public mass shootings have occurred in various places and situations, such as schools, churches, malls, and concerts, and have targeted people from different backgrounds and ages. Read it for free on Archive: https://archive.ph/u18Ne.
Online daters are less open-minded than their filters suggest
The Economist
This article is about how online daters use filters to exclude unwanted groups, but still show preferences for certain traits when they see their prospects. The document provides data from The League, an American dating site for educated professionals, to illustrate how filtering choices vary by gender, age, height and race.
We find that online daters might find better matches if they were more open-minded and gave a chance to more candidates who pass their filters. Open the website and play around. Read on for more insights on Archive: https://archive.ph/W0LzA.
Learning R Markdown
Dr Umberto Noè and Dr Josiah King
These online notes on R Markdown will “take you from zero to RMarkdown-hero!” There are eight chapters that cover useful things about R Markdown.
Intuitively Understanding Variational Autoencoders (VAE)
Irhum Shafkat
VAE are powerful generative models. The article starts with a review of standard autoencoders, which are neural networks that compress and reconstruct their own input, and shows how they can be used for dimensionality reduction and feature extraction.
The main idea of VAEs is to regularize the distribution of the encodings produced by the encoder network, so that they can be easily sampled and interpolated in a continuous latent space.
Four Packages
memer is a package for generating memes.
meme_get("DistractedBf") %>%
meme_text_distbf("tidyverse", "new R users", "base R")
emo lets you insert emojis into RMarkdown. (I’ve never needed a separate package for this task though; copy + paste works just fine.)
emojifont is another package for inserting emojis into RMarkdown and ggplot2.
praise: Are you looking for compliments? This package can help.
praise::praise()
> [1] "You are super-excellent!"
Three Jargons
Autoencoders: Autoencoders are a type of neural network used for unsupervised learning. They are designed to encode input data into a lower-dimensional representation, and then decode it back into its original form. This technique can be used for tasks like data compression, noise reduction, and image generation.
Convolutional Neural Networks: Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are a type of neural network that are commonly used for image and video recognition tasks. CNNs use a series of convolutional layers to extract features from the input data, followed by fully connected layers for classification or regression.
RLHF stands for Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback. It's a type of machine learning where a human evaluator provides feedback to the learning agent in addition to the reward signal received from the environment. This can help the agent learn more quickly and effectively. It has potential applications in education, healthcare, and robotics.
Two Tweets